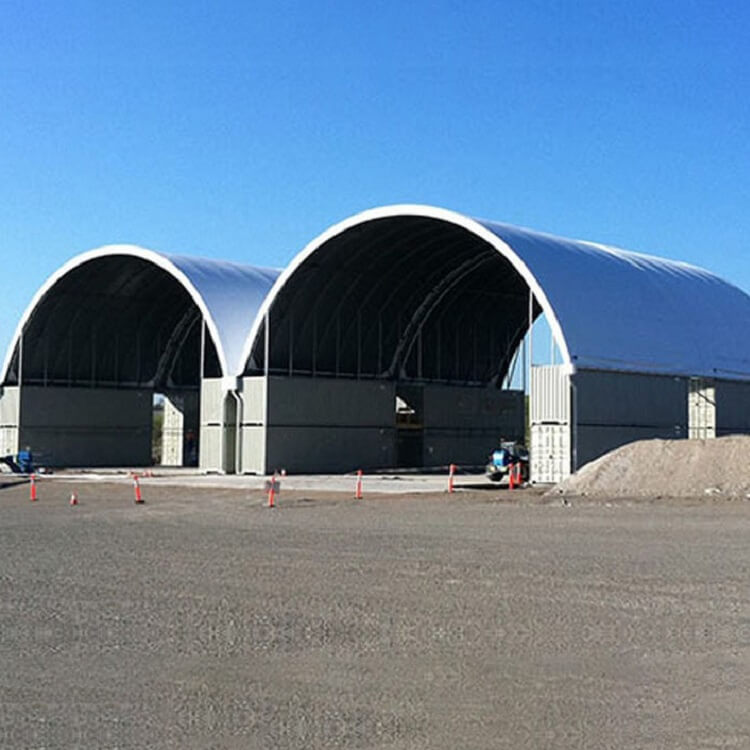
Design Services
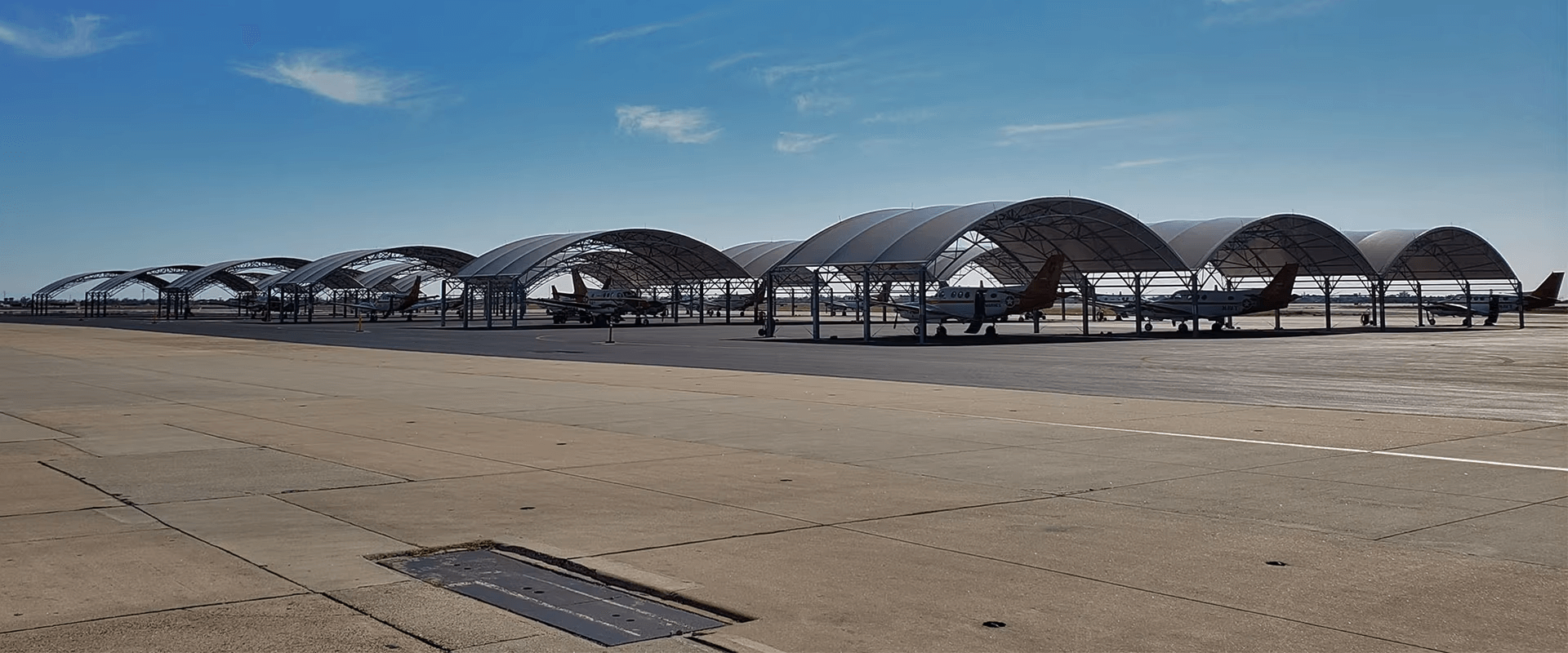

Understanding Containers and Shelters: Design, Applications, and Benefits
Containers and shelters are highly versatile structures that serve a wide range of applications across industries. Combining portability, durability, and cost-effectiveness, these structures have become indispensable for storage, temporary housing, industrial use, and even as emergency solutions. This article explores the fundamental characteristics, types, and advantages of containers and shelters.
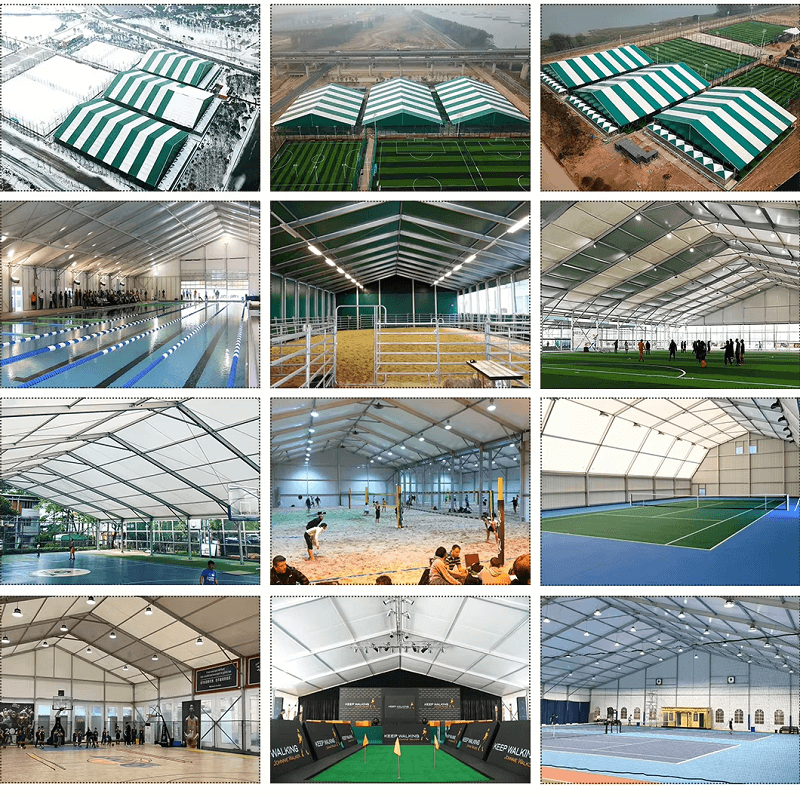

1. Containers: Characteristics and Applications
- 1.1 Design and Features
- Shipping containers are made of corten steel, which is resistant to corrosion and weathering. They are designed to be stackable and robust, making them suitable for repurposing. Common dimensions include:
- 20-foot containers (6.06m x 2.44m x 2.59m)
- 40-foot containers (12.19m x 2.44m x 2.59m)
- Shipping containers are made of corten steel, which is resistant to corrosion and weathering. They are designed to be stackable and robust, making them suitable for repurposing. Common dimensions include:
Additional features include secure doors, insulated walls (in refrigerated containers), and modular compatibility.
- 1.2 Applications
- Storage Units: Containers are widely used as secure, weatherproof storage for goods, tools, and materials.
- Workspaces and Offices: With minor modifications, containers can be transformed into portable offices or workshops.
- Housing Solutions: Modular container homes offer an affordable and sustainable alternative to traditional construction.
- Emergency Shelters: Containers are used for disaster relief due to their rapid deployability and durability.
2. Shelters: Characteristics and Applications
Shelters are lightweight, semi-permanent structures designed to provide protection from environmental elements. They range from fabric-covered domes to steel-framed canopies.
- 2.1 Types of Shelters
- Container Shelters: These are arched or flat-roofed structures installed on shipping containers, often used for agricultural, industrial, or military applications.
- Fabric Shelters: Built using steel frames and high-strength fabric covers, these shelters are easy to assemble and relocate.
- Emergency Shelters: Temporary structures designed for quick deployment in disaster-stricken areas.
- 2.2 Application
- Industrial Use: Shelters provide a cost-effective solution for warehouses, equipment storage, and vehicle maintenance bays.
- Agricultural Use: Farmers use shelters to protect crops, livestock, and machinery from harsh weather.
- Event Spaces: Fabric shelters serve as temporary venues for events, exhibitions, and workshops.
- Military and Emergency Use: Portable shelters are vital in remote operations or disaster zones for housing, medical facilities, and command centers.
3. Benefits of Containers and Shelters
- 3.1 Durability and Weather Resistance
- Containers offer unparalleled strength, capable of withstanding extreme conditions such as high winds, snow, and earthquakes.
- Modern shelters use UV-resistant and waterproof materials, making them suitable for harsh environments.
- 3.2 Cost-Effectiveness
- Repurposing containers reduces construction costs and waste.
- Shelters provide a cheaper alternative to permanent buildings while still offering adequate protection.
- 3.3 Flexibility and Mobility
- Both containers and shelters are modular and portable, allowing for easy relocation and expansion.
- Shelters can be assembled and dismantled with minimal labor and time investment.
- 3.4 Environmental Sustainability
- Using refurbished containers minimizes steel waste and promotes recycling.
- Fabric shelters have a smaller environmental footprint compared to traditional construction methods.
4. Innovations in Containers and Shelters
- Technological advancements have expanded the functionality of containers and shelters:
- Solar Integration: Containers and shelters can be equipped with solar panels for off-grid energy solutions.
- Smart Systems: IoT sensors monitor temperature, humidity, and structural integrity, especially for storage and housing applications.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Recycled materials and biodegradable fabrics are becoming increasingly popular for shelters.
5. Key Considerations for Selection
- When choosing between a container or a shelter, the following factors should be evaluated:
- Purpose: Long-term storage may require a container, while temporary needs are better served by shelters.
- Location: Consider environmental conditions, such as wind load and temperature, to determine the right material and design.
- Budget: While shelters are generally cheaper upfront, containers provide long-term durability and higher resale value.
- Customization: Both containers and shelters can be modified for insulation, ventilation, and specific layouts to meet unique requirements.
6. Conclusion
Containers and shelters are transformative solutions that cater to a myriad of industries, from agriculture and construction to emergency relief and housing. Their durability, adaptability, and cost-efficiency make them essential for modern infrastructure needs. As technology advances, the integration of smart features and sustainable materials will further enhance their utility, ensuring that these structures remain at the forefront of innovation.
For businesses or individuals considering these solutions, consulting with specialized providers ensures tailored designs that maximize functionality and value.